What You Need To Know
Monkeypox is a rare disease caused by infection with the monkeypox virus. Monkeypox virus is part of the same family of viruses as variola virus, the virus that causes smallpox. Monkeypox symptoms are similar to smallpox symptoms, but milder, and monkeypox is rarely fatal.
- CDC is tracking an outbreak of monkeypox that has spread across several countries that don’t normally report monkeypox, including the United States.
- The monkeypox virus is spreading mostly through close, intimate contact with someone who has monkeypox.
- You can take steps to prevent getting monkeypox and lower your risk during sex.
- CDC recommends vaccination for people who have been exposed to monkeypox and people who are at higher risk of being exposed to monkeypox.
- If you have any symptoms of monkeypox, talk to your healthcare provider, even if you don’t think you had contact with someone who has monkeypox.
- CDC is urging healthcare providers in the United States to be alert for patients who have rash illnesses consistent with monkeypox.
Infections with the type of monkeypox virus identified in this outbreak—the West African type—are rarely fatal. Over 99% of people who get this form of the disease are likely to survive. However, people with weakened immune systems, children under 8 years of age, people with a history of eczema, and people who are pregnant or breastfeeding may be more likely to get seriously ill or die.
How Monkeypox Spreads
Monkeypox spreads in a few ways.
- Monkeypox can spread to anyone through close, personal, often skin-to-skin contact, including:
- Direct contact with monkeypox rash, scabs, or body fluids from a person with monkeypox.
- Touching objects, fabrics (clothing, bedding, or towels), and surfaces that have been used by someone with monkeypox.
- Contact with respiratory secretions.
- This direct contact can happen during intimate contact, including:
- Oral, anal, and vaginal sex or touching the genitals (penis, testicles, labia, and vagina) or anus (butthole) of a person with monkeypox.
- Hugging, massage, and kissing.
- Prolonged face-to-face contact.
- Touching fabrics and objects during sex that were used by a person with monkeypox and that have not been disinfected, such as bedding, towels, fetish gear, and sex toys.
- A pregnant person can spread the virus to their fetus through the placenta.
It’s also possible for people to get monkeypox from infected animals, either by being scratched or bitten by the animal or by preparing or eating meat or using products from an infected animal.
A person with monkeypox can spread it to others from the time symptoms start until the rash has fully healed and a fresh layer of skin has formed. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
Scientists are still researching:
- If the virus can be spread when someone has no symptoms
- How often monkeypox is spread through respiratory secretions, or when a person with monkeypox symptoms might be more likely to spread the virus through respiratory secretions.
- Whether monkeypox can be spread through semen, vaginal fluids, urine, or feces.
Monkeypox Symptoms
People with monkeypox get a rash that may be located on or near the genitals (penis, testicles, labia, and vagina) or anus (butthole) and could be on other areas like the hands, feet, chest, face, or mouth.
- The rash will go through several stages, including scabs, before healing.
- The rash can initially look like pimples or blisters and may be painful or itchy.
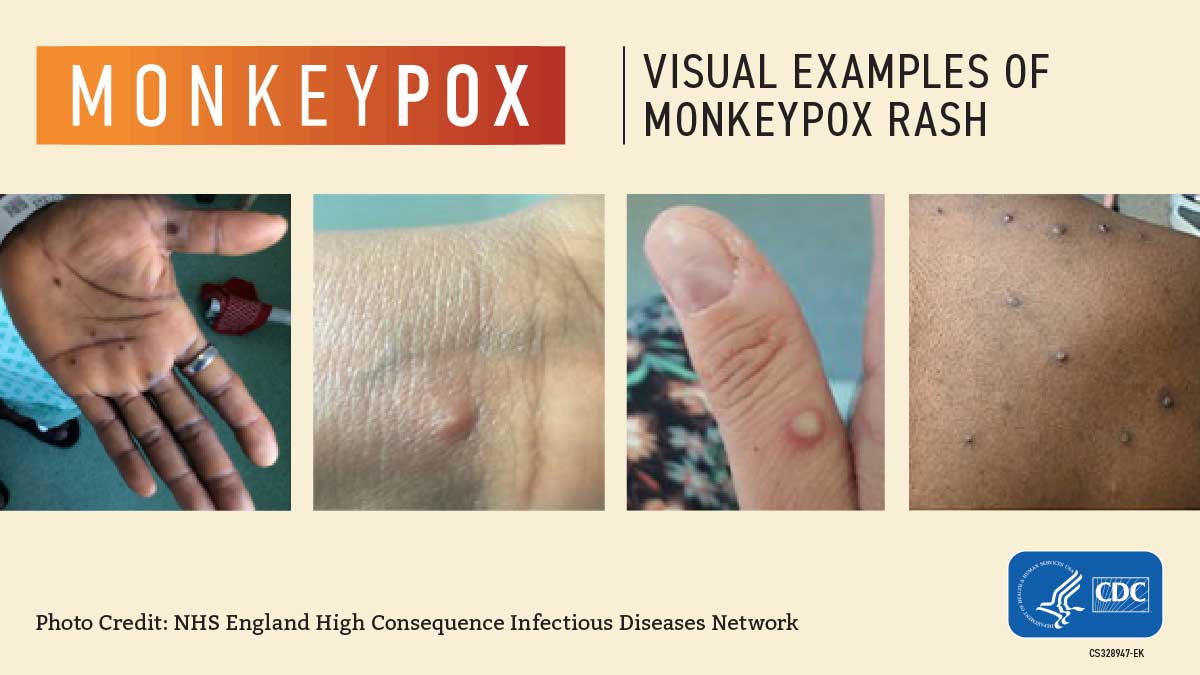
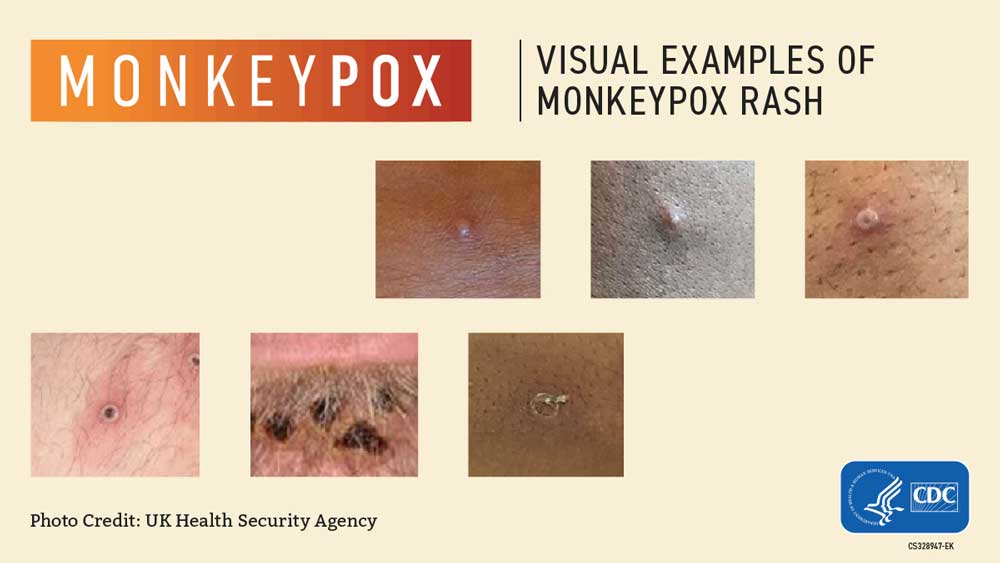
Other symptoms of monkeypox can include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion
- Muscle aches and backache
- Headache
- Respiratory symptoms (e.g. sore throat, nasal congestion, or cough)

You may experience all or only a few symptoms:
- Sometimes, people have flu-like symptoms before the rash.
- Some people get a rash first, followed by other symptoms.
- Others only experience a rash.
How long do monkeypox symptoms last?
Monkeypox symptoms usually start within 3 weeks of exposure to the virus. If someone has flu-like symptoms, they will usually develop a rash 1-4 days later. Monkeypox can be spread from the time symptoms start until the rash has healed, all scabs have fallen off, and a fresh layer of skin has formed. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
- Avoid close contact, including sex or being intimate with anyone, until you have been checked out by a healthcare provider.
- If you don’t have a provider or health insurance, visit a public health clinic near you.
- When you see a healthcare provider, wear a mask, and remind them that this virus is circulating in the area.
Monkeypox Treatment
There are no treatments specifically for monkeypox virus infections. However, monkeypox and smallpox viruses are genetically similar, which means that antiviral drugs and vaccines developed to protect against smallpox may be used to prevent and treat monkeypox virus infections.
Antivirals, such as tecovirimat (TPOXX), may be recommended for people who are more likely to get severely ill, like patients with weakened immune systems. If you have symptoms of monkeypox, you should talk to your healthcare provider, even if you don’t think you had contact with someone who has monkeypox.
Monkeypox Prevention
When thinking about what to do, seek out information from trusted sources like the local health department. Second, consider how much close, personal, skin-to-skin contact is likely to occur at the event you plan to attend. If you feel sick or have a rash, do not attend any gathering, and see a healthcare provider.
Talk with your partner about any monkeypox symptoms and be aware of any new or unexplained rash or lesion on either of your bodies, including the mouth, genitals (penis, testicles, vulva, or vagina), or anus (butthole). If you or your partner has or recently had monkeypox symptoms, or you have a new or unexplained rash anywhere on your body, do not have sex and see a healthcare provider. In some cases, symptoms may be mild, and some people may not even know they have monkeypox.
If you or a partner has monkeypox or think you may have monkeypox, the best way to protect yourself and others is to avoid sex of any kind (oral, anal, vaginal) and kissing or touching each other’s bodies—while you are sick. Especially avoid touching any rash. Do not share things like towels, fetish gear, sex toys, and toothbrushes.
Even if you feel well, here are some ways to reduce your chances of being exposed to monkeypox if you are sexually active:
- Take a temporary break from activities that increase exposure to monkeypox until you are two weeks after your second dose. This will greatly reduce your risk.
- Limit your number of sex partners to reduce your likelihood of exposure.
- Spaces where sexual contact with multiple partners occurs—are more likely to spread monkeypox.
- Condoms (latex or polyurethane) may protect your anus (butthole), mouth, penis, or vagina from exposure to monkeypox. However, condoms alone may not prevent all exposures to monkeypox since the rash can occur on other parts of the body.
- Gloves (latex, polyurethane, or nitrile) might also reduce the possibility of exposure. The gloves must cover all exposed skin and be removed carefully to avoid touching the outer surface.
- Avoid kissing or exchanging spit since monkeypox can spread this way.
- Be aware that monkeypox can also spread through respiratory secretions with close, face-to-face contact.
- Remember to wash your hands, sexual aids, and any fabrics (bedding, towels, clothes) after having sex. Learn more about infection control.
